The pike is the king of French waters. This fish is the stuff of dreams for many anglers, and the size, search and fight for it are exceptional. But to fish for this predator, you need to know all about it. Here's an article summarising everything you need to know about pike and pike fishing in France.

Origins of the pike
The pike (Esox lucius) is a carnivore belonging to the family Esocidae. This fish is caught in many parts of the world, particularly in Europe, North America and Asia.
The word pike "comes from the Latin barrus" which means coarse "or brutal" . The name reflects the physical characteristics of this fish, notably its large head and powerful jaws. The word has been borrowed from Latin by many languages. In France, the word is also used to describe other animals, such as the wild pig. However, it is mainly associated with fish.
There are only one species of pike on the planet: Esox lucius. However, there are several subspecies or varieties that differ in size, colour and habitat.
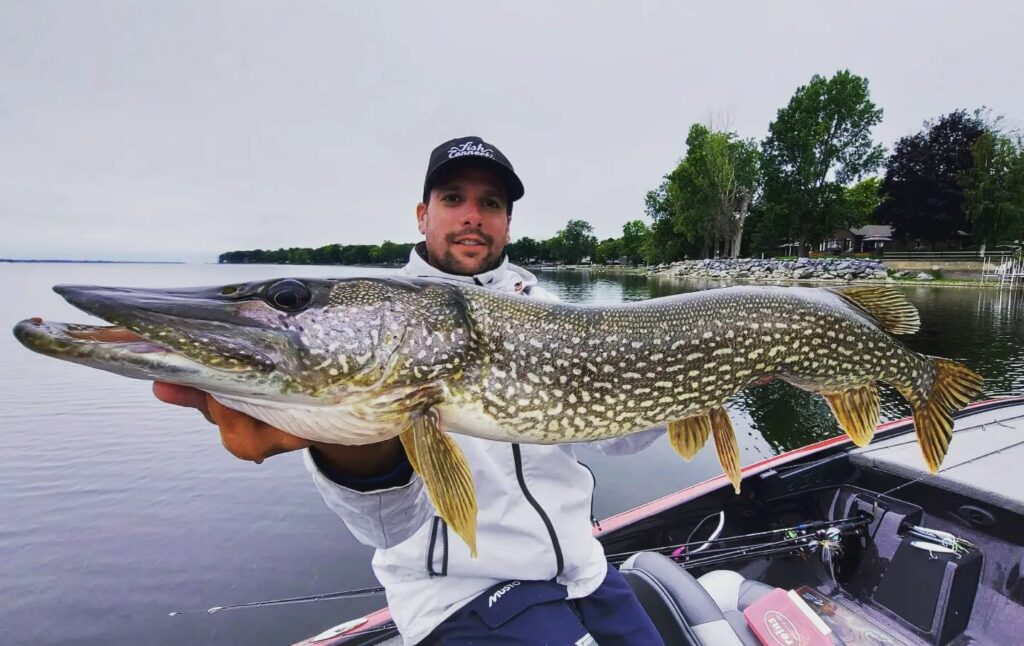

Here are some examples of pike subspecies:
- North American pike (Esox lucius americanus) : This subspecies is commonly known as the "northern pike". It is found in many North American countries, including the United States, Canada and Mexico. It is dark grey-green in colour and generally measures between 60 and 100 cm in length.
- Caucasian pike (Esox lucius ciscaucasicus) : This subspecies of pike is endemic to the Caucasus region of Asia. It has a dark grey-green colour and generally measures between 60 and 100 cm in length.
It is important to note that these subspecies are very similar. They are difficult to distinguish without in-depth genetic analysis. In addition, there are many other subspecies that can vary depending on their habitat and food.
Pike morphology
The pike has an elongated, streamlined shape, with a broad head and powerful jaw. Its head is generally wider than its tail and its mouth has sharp teeth. Its body is covered in scales and its colour varies from grey to dark green, with black or brown markings along its back and flanks. Its tail is long and narrow, with lateral lobes that give it a "V" shape. Pike are generally between 60 and 120 cm long and can weigh up to 20 kg.
Sharp teeth
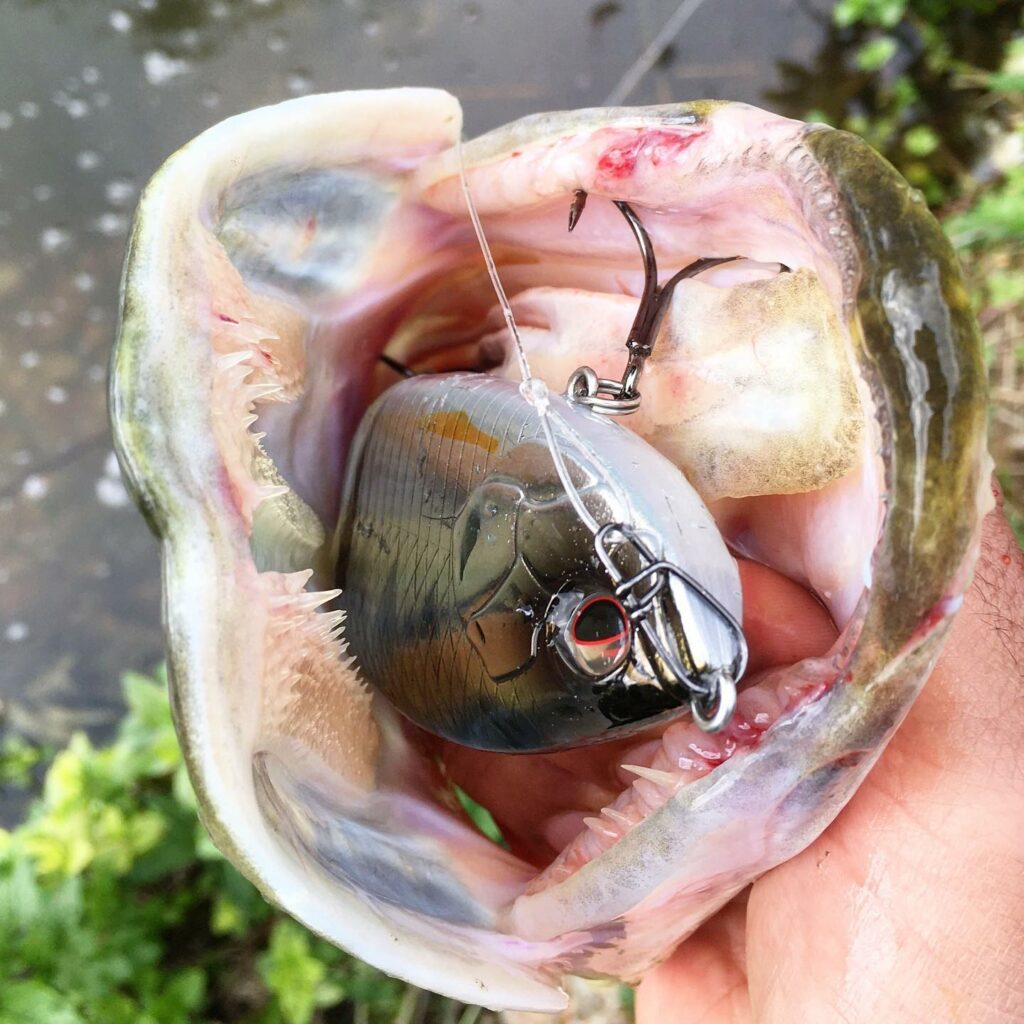

Pike has around 700 teeth, spread across its upper and lower jaws. These teeth are sharp and designed to grip and tear prey.
The teeth are arranged so that the teeth of the upper jaw are smaller and thinner than those of the lower jaw. This allows the pike to grasp and hold its prey better, while inflicting severe wounds.
Esox Lucius also has two rows of teeth on its tongueThe tongue of the pike is covered with small growths called papillae. The pike's tongue is covered with small growths called papillae. These give the tongue a rough texture and help it to grip its prey better.
The view
Pike have eyes that allow them to see underwater quite clearly. However, its vision is not as good as that of other fish. Its vision is mainly adapted to detecting movements and shapes, rather than recognising precise details.
The Pike has round, bulging eyes that enable it to see in all directions. Its eyes are located on the side of its head and are protected by mobile eyelids. These enable them to close when moving at high speed or in bright light.
This fish also has an adaptive vision system that enables it to adapt quickly to different light conditions underwater. Its vision is better performance in shallow, clear waterswhere it is better able to detect its prey. On the other hand, its vision is less good in dark or murky waters, where it has to rely more on its other senses to hunt.
The sensory organs
It has several sensory organs that enable it to detect its prey. For example, it has sensitive fins that detect the vibrations and movements of its prey.

Finally, the Pike has a highly developed olfactory system that enables it to detect the odours of its prey. Its mouth has glands that produce chemicals that enable it to detect the scents of its prey, even at great distances.
The pike's lateral line is also a sensory organ that enables it to detect the vibrations and movements of its prey. It is located along the body and is made up of sensitive sensors called "linear scales". These sensors are highly sensitive to vibration and movement. This enables esox lucius to detect the movements of its prey even in dark or murky waters.
The pike's lateral line is a very important organ for its survival. It enables them to hunt their prey and locate it even in conditions of reduced visibility. It also plays an important role in pike communication and orientation. It enables them to perceive the vibrations and movements of other fish.
Service life
The The lifespan of a pike depends on several factors: habitat quality, health, food. In general, this fish can live up to 15 years in its natural habitat.although some individuals may live longer.
Pike reproduction
The Pike reaches sexual maturity at between 4 and 7 years of ageThis depends on the habitat and food available. From this age onwards, they are able to reproduce and lay eggs. Females can lay up to 100,000 eggs per breeding season. However, only a small proportion of these eggs will result in adult fish.
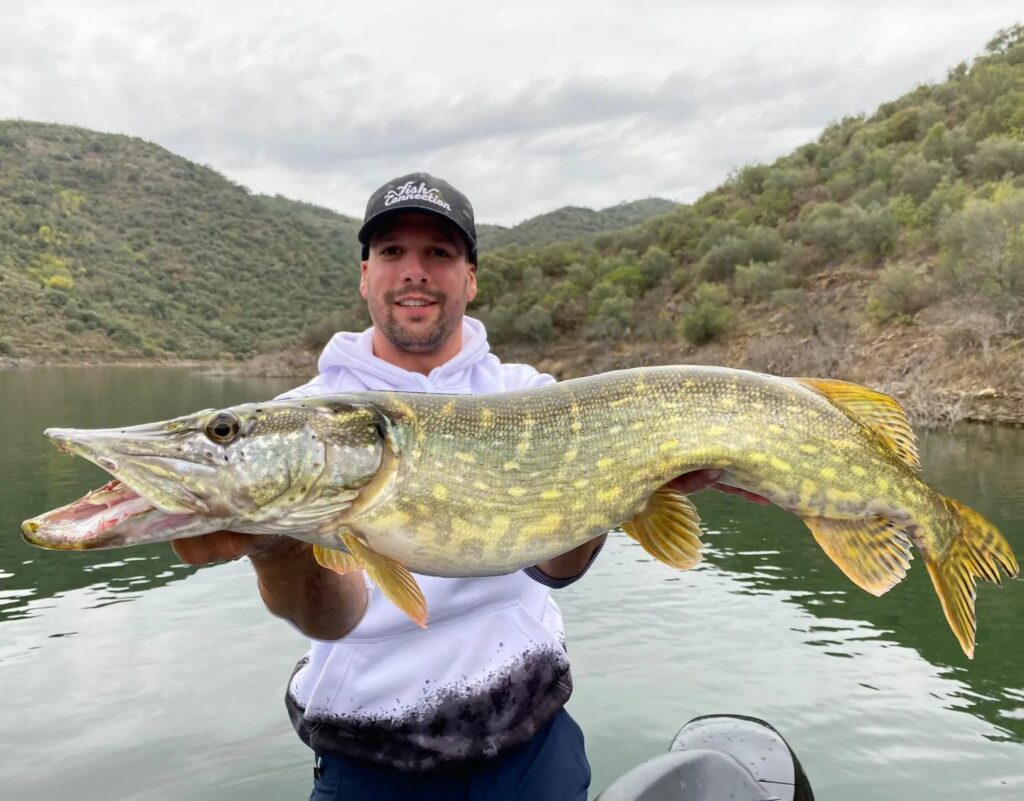

The pike's spawning period depends on the habitat in which it lives. In general, this carnivore reproduces in spring or early summer, when the water levels are low. water temperatures reach around 12 to 15 degrees Celsius. However, the exact breeding season can vary from region to region and from year to year.
Before reproduction, pike gather in small groups and start looking for a partner. Males and females rub against each other and move into a mating position known as "nesting". The females then lay their eggs, which are fertilised by the males.
Pike eggs are generally laid in nests dug into the water bottom, often near solid structures such as rocks or branches. The males protect the nest until the eggs hatch, usually after 2 to 3 weeks. The fry are very small and feed on plankton until they are big enough to hunt small fish.
How can you tell a male from a female?
There are several ways to tell a male pike from a female. Here are a few signs to help you tell them apart:
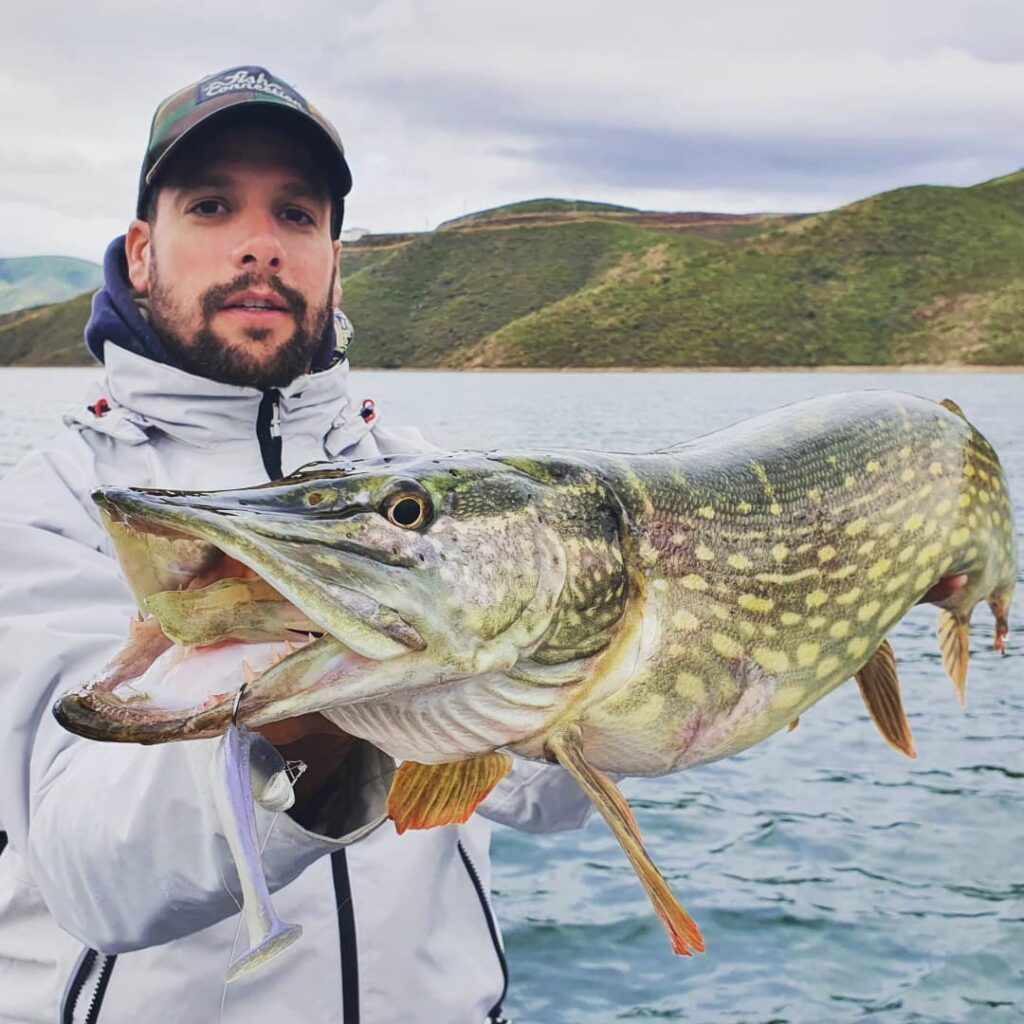

- Size : Females are generally larger than males. Males generally measure between 60 and 80 cm in length. Females can reach up to 120 cm in length.
- Head shape : Females generally have a larger, more rounded head than males.
- The anal fin : Females generally have a larger, more rounded anal fin than males.
- Caudal fin shape : Females generally have a narrower, more pointed caudal fin than males.
It is important to note that these signs are not always easy to spot and that the best way to distinguish a male from a female is to compare them side by side. What's more, some individuals may not match the typical characteristics of their sex, which can make it difficult to tell them apart.
Pike habitat
The pike is a freshwater fish found in many countries around the world. It is particularly popular in Europe, North America and Asia. It is found in many types of aquatic environment: lakes, rivers, streams and ponds.
Pike prefer calm, shallow waters with abundant aquatic vegetation. It needs solid structures, such as rocks or branches, to hide and protect itself. It also needs good sources of food, such as smaller fish, frogs and birds.
It is a solitary, territorial fish that prefers to live alone or in small groups. It can adapt to many types of habitat, but is generally more abundant.
Power supply
The pike is an opportunistic predator that feeds mainly on fish. However, it can also eat other animals such as frogs, birds and even small mammals. To catch its prey, it uses different techniques depending on the target species and its environment.
Here are some examples of attack techniques used by pike:
- Ambush attack. The pike is perfectly camouflaged in weed beds or shallows and waits for its prey to pass close by. It can then leap to catch its prey between its jaws.
- The attack in pursuit. When its prey tries to flee, the pike can pursue it at high speed by using its caudal fin to propel its body through the water.
- Attacking in groups. In some cases, pike may work with other individuals of their species to hunt their prey. For example, they may surround a trout and prevent it from escaping by cutting off all escape routes.

As mentioned, Esox Lucius is also able to detect vibrations in the water. This enables it to detect the presence of potential prey even in darkness or murky water. Once it has spotted prey, it can move quickly to catch it.
How often it feeds depends on several factors: size, physical condition and availability of food in its habitat. In general, adults feed less frequently than young. This is because they need less energy to maintain their body mass and temperature. However, they may be able to feed more intensively when they are breeding or during periods of stress, such as food shortages or the presence of predators.
Fishing and regulations
Pike fishing in France is governed by the law on fishing and by departmental and regional regulations. Here are some of the main rules that apply to pike fishing in France:

- Minimum catch size. The minimum size for catches varies between regions and departments. In general, the minimum size is 60 cm. However, it may be higher in certain regions or at certain times of the year.
- Catch quotas. Some regions and fishing zones have catch quotas for pike. These limit the number of fish that anglers can catch each day or week.
- Closed periods. There are closed seasons for pike fishing, generally during the breeding season.
- Authorised fishing methods. Only certain fishing methods are authorised for pike, such as angling, live fishing and lure fishing. Net and seine fishing are generally prohibited.
Opening and closing dates for pike fishing 2023
Pike fishing generally opens on 1st weekend in May in 2nd category rivers. Pike are generally closed on Last Sunday in January.
This year, pike fishing will open on 29 April 2029 and close on 28 January 2024.
However, we recommend that you find out about the rules in force in the region where you fish, and that you comply with any quotas and closed seasons. Failure to comply with these rules may result in penalties such as a fine or suspension of your fishing licence.
When can you fish for pike?
As long as you fish for this fish during the legal opening period, you can fish from 30 minutes before sunrise and 30 minutes after sunset. Fishing for pike at night is therefore prohibited, except in the event of a prefectoral decree.
Useful links to complete this article on pike:
Pike spinnerbait: 5 essential spinnerbaits for pike fishing
Pike crankbait: 5 essential pike crankbaits
Pike jerkbait: our selection of 5 pike jerkbaits
Pike lures: 10 pike lures to have in your box of lures


Pingback: Lb, Oz: Everything you need to know about these fishing weights
Pingback: Inch, Foot: Everything you need to know about these length measurements for fishing
Pingback: Pike Stickbait - 5 top stickbaits for pike fishing